Now I will explain the concept of 2 stroke engine and 4 stroke gasoline engines.
Let’s start in the vision of Sanchit Saxena and make it simple.
How 2 stroke engine works
 |
| 2 stroke engine(gasoline) |
This diagram shows us the working of 2 stroke principle,
before we start some important things we need to know: Spark plug, Transfer
port, connecting rod, crank case, Inlet port, exhausts port, stroke.
- Spark plug It is a device that ignites the mixture of fuel and air with the help of current; it is located in head of I.C engine.
Transfer
port
It is related to the transformation of fuel
and air mixture to the upper chamber due to compression force.
Connecting
rod It’s a rod that connects piston to crank shaft, together
with the crank they form a simple mechanism that converts reciprocating motion
into rotating motion.
- Crank case -The area around the crankshaft is called the crankcase; it is located below the cylinders, it helps to pre-compress the mixture of fuel and air.
As we know
that in 2 stroke engine has 2 stroke i.e. upstroke and down stroke. Let’s start,
in upward stroke (B.D.C to
T.D.C)first the previous stroke fuel mixture is compressed and ignited by the
spark plug, when it produce spark in cylinder, the mixture of fuel and air is
burn and converted into a hot gases at this stage we get power stroke. Hot burned
gases expand and they push down the piston. On other side the mixture of fuel
and air is enter into the crankcase through inlet port and it is pre-compressed
by piston in crankcase.
Downward stroke (T.D.C to B.D.C) – In this stroke the burned fuel is pushed out by
compressed fuel mixture and side by side the pre-compress fuel mixture is
transfer through transfer port then it is compress in cylinder and then it
ignite by the spark plug. Generally these types of I.C engine used in previous
era, some best bikes and scotoors of 2 strokes are Yamaha rx 100, Bajaj Chetak.
And the car is Subaru 360.
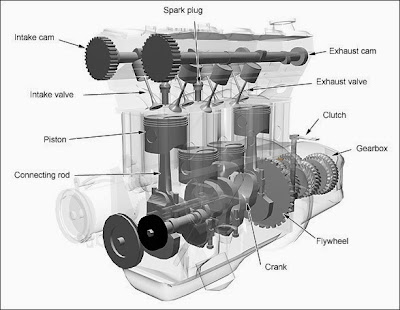
How 4 stroke engine works
At first we
discuss about the following terms which are used in 4 stroke engine works
- Intake valves – The function of intake valves is to allow the fuel and air mixture into the cylinder, these valves are located in the cylinder head of I.C engine, these valves are control by Cam shaft.
- Exhaust valves – The function of exhaust valves is to escape the burned gases from a cylinder. These valves are located in the cylinder head of I.C engine; these valves are control by Cam shaft.
Let’s start as we know that 4 stroke engine having 4 strokes.








.jpg)




.jpg)